Image : National Cancer Institute.
The incidence of breast cancer is increasing all over the world and India in particular has been fast to catch up with the increasing trend. In fact it's so fast that breast cancer has overtaken cervix cancer and has become the most common cancer in urban Indian women. At present it is affecting 1 in 25 women in the major Indian cities. More worrisome is the higher rate of death in India than the western countries e.g US where the incidence is rather more than us (1 in 8 women). The main or prime factor for higher Indian mortality is the ''advanced or late nature of the presentation.
''Self exam of breast'' and ''FNAC'' are the only 2 ways out for the early diagnosis and treatment. A 30% reduction in mortality can be achieved by these 2 simple means. Contrary to the popular belief ''Mammography'' may not save as many lives as proposed - a conclusion derived from 3 decades of screening mammogram, recently published in New England Jl. of Medicine.
The survival rate in breast cancer has dramatically improved mainly because of self breast exam, increased awareness, early FNAC and the paramount advances in the treatment of breast cancer. The accelerated research that has led to much better understanding of the disease and a wider variety of treatment choices/options that doctors can mix and match to tailor therapy for a particular patient.In just the past decade, it has even become possible to target drugs to specific molecules within tumors that help to drive the disease.
*** Increased awareness leads to early detection ***.
A more prudent approach would be to enhance ''breast awareness'' of the Indian population, a baseline mammogram of all women at the age of 40 and then on yearly basis with prompt FNAC in case of any lump/bump.
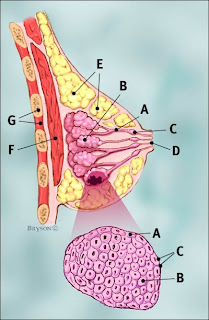
Normal Anatomy of Breast. :-
The breast is a modified skin appendage, functional in females and rudimentary in males.Breast is composed of two types of tissue elements : (1) epithelial and (2) stromal.
Epithelial element is also called as glandular tissue and it is arranged in lobules (pockets).
Stromal element is made up of fat,fibrous and muscular tissues.
During menstrual cycle normally,the breast is smallest in size on days 4-7, and then begins to enlarge,under the influence of estrogen hormone and later progesteron and prolactin hormones.Maximum breast size occurs just prior to the onset of menses.This is physiologically normal and must be kept in mind during self exam.of breast.

The glandular tissue is depicted above as purple colored pockets or lobules and the supporting or stromal part by yellow colored fat mainly.The base of each breast is made up of a large chest muscle known as pectoralis major muscle which further rests on our rib cage.
The normal breast is not round,but has a "tail" of breast tissue extending up into the axilla (arm pit).This is important because diseases/cancer can arise there just as they occur in other areas of breast.Therefore,during breast exam.this tail area must also be examined and palpated.
In a fully developed non lactating female breast,the epithelial component comprises nearly 10% of the total breast volume while in a lactating(breast feeding) breast it may make up to 60-80% of whole breast mass.
This epithelial part of breast is most significant pathologically since majority of breast diseases esp. breast cancer always arise from it.
In above diagrams,the underlying reddish strands or bands are fibers of muscles (pectoralis major) over which breast tissue normally rests and purple colored element is epithelial lobules--main originator of breast cancer and other lesions/diseases of breast.(cysts-fluid filled cavities).
A = Duct, B = Lobule, C = Dilated part of duct to hold milk, D = Nipple, E = Fat, F = Muscle bed beneath the breast, G = Chest wall or rib cage.
Normal drainage pathway of breast.
Anything happening abnormal in breast is drained out through small channels (lymphatics or lymph ducts) with lymph stations (lymph nodes) in the way to your arm-pit. Primarily through this drainage system the breast cancer spreads first to the arm pits and then further to other parts of body via further ramifications of this system.
Etiology/Risk Factors of Breast Cancer
Exact etiology of breast cancer still remains elusive.However there are risk factors which are considered significant in its etiology.
(1). Geography : Breast cancer is about six times higher in developed countries than developing countries,with the notable exception of Japan.These geographic differences are related to consumption of large amount of animal fats and high caloric diet by Western population than the Asians and Africans.
(2). Age : The risk of getting breast cancer increases with age as depicted in the above chart.A woman who lives to age 90 has a lifetime risk of about 14.3% or one in seven.The incidence of breast cancer is highest in the peri menopausal age (age when the menstrual cycle ceases in women i.e. 40-50 yrs).It is uncommon before the age of 25 years.But when it occurs in young women, it is more aggressive and dangerous.
(3). Genetic factors(Heredity) : Recently,much work has been done on the influence of family history and inherited mutations(gene changes) in breast cancer.In 5% of breast cancer cases,there is a strong inherited familial risk.
(i) Family history (20-30% cases)--First degree relatives(mother,sister,daughter)of women with breast cancer have 2 to 6 fold higher risk of development of breast cancer.This risk further increases with number of close relatives with breast cancer--(having 2 first degree relatives increases her risk about 5-folds).,younger age at the time of development of cancer,both side breast cancers,and higher risk cancer families having both breast and ovary cancers.
(ii) Inherited mutations(gene changes)--About 5-10 % breast cancers have been found to have inherited mutations.These include : p53,BRCA-1,and BRCA-2. Family members who harbor mutations in these genes have a 60% to 80% risk of developing breast cancer in their lifetimes.
(iii)Personal history of breast cancer :--A woman with cancer in one breast has a 3 to 4 fold increased risk of developing a new cancer in the other breast or in another part of the same breast..This is different from a recurrence(return) of the 1st cancer.
(4). Estrogen (female hormone) excess : Excess of estrogen hormone produced in the body or given from outside as pills is an important factor in the development of breast cancer.Normal breast tissue has many estrogen receptors and bind this hormone in it.
Evidences of estrogen excess being the cause of breast cancer are as follows :
(1).Women with prolonged reproductive life,with menarche (age at onset of menses) setting in at an early age (before age 12) and menopause(age at cessation of menses) relatively late (after age 55) have greater risk due to a higher lifetime exposure to estrogens.
(2)Higher risk(triple) in unmarried and nulliparous(women without children) women than in married and multiparous (women with many children) women.
(3) Women with first childbirth at a late age (over 30 years) are at greater risk.Having the 1st child after age 30 doubles the risk compared to having first live birth at age less than 25. Never having children triples the risk.
(4) Lactation(breast feeding) is said to be protective and reduce the risk of breast cancer (4.3% lowered risk per breastfeeding year).This is because breastfeeding reduces a woman's total number of life time menstrual cycles and hence reduced exposure to estrogens.
(5) Removal of both ovaries help protect against cancer.
(6) Estrogen hormone replacement therapy (HRT) after menopause result in increased risk(relative risk of 1.35 for women who had used HRT for 5 or more years after menopause.
(5). Environmental and dietary factors : Many such contributors to development of cancer breast are as follows :
(1) Tail Pipe Toxins :
Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAH) released from vehicular exhausts are at top of the list and are a potent breast carcinogens.
(2) Tobacco Smoke :
Tobacco smoke also contain many polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAH) similar to tail pipe exhaust like Dibenzanthracene and Dibenzochrysene which are potent cancer causing agents.Even breathing secondhand smoke(passive smoking) increases breast cancer risk by 70% in younger women.It is most problematic between puberty and 1st child birth because breast cells are not fully developed or differentiated in this phase of life and are most sensitive to chemical carcinogens.
(3) Industrial Exhaust :
Again early life exposure to PAH released from industrial waste and exhaust increases the risk of middle or later age breast cancer.
(4) Drinking Alcohol :
Natural cancer causing substances (carcinogens) primarily "Urethanes" are found in alcohol including wine and beers.Compared with non-drinkers,women who consume 1 alcoholic drink per day have a very small increased risk.Those who have 2 to 5 drinks daily,have about 1.5 times the risk of women who drink no alcohol.Recent study also showed : each additional 10 gm of alcohol consumed daily(about one drink) is equated to an added 9 % risk of breast cancer.Approximately 6% of breast cancers reported in UK each year could be prevented if drinking was reduced to a very low level (i.e. less than 1 unit per week).
The American cancer society recommends that women limit their consumption of alcohol to no more than one drink a day.
(5) Food Toxins :
Pesticides tainting on crops ,antibiotics fed to poultry,hormones injected into cattle for milking and other purposes,and milk sold in US (banned in Canada and Europe) containing Insulin like growth factor I, may put increased risk of breast cancer.Similarly grilled or charred meat and fish contain mutagens (gene altering agents or carcinogens) formed during grilling process. Acrylamides found in French fries, breads and cereals cooked at very high temp.also pose cancer problems.
Fat intake : Recent research suggests that low fat diets may significantly reduce the risk of breast cancer as well as its recurrence.Animal fat has been found to be more risky than vegetable fat.Vitamin D is related to reduced risk of breast cancer.Brassica vegetables intake has been shown to be inversely related to breast cancer development.
In 2009 a case-control study of 2,018 women suggested that women who consumed mushrooms had an approx. 50% lower incidence of breast cancer.Women who consumed mushrooms and green tea had a 90% lower incidence of breast cancer.
In 2008 studies have shown that a very high consumption of omega-6 polyunsaturated fatty acids(PUFA),which are found in soyabean oil, corn oil-the most consumed in USA,and sunflower oil may increase the likelihood that postmenopausal women will develop breast cancer.
It is recommended that women should eat a healthy diet with emphasis on plant sources.This includes eating 5 or more servings of vegetables and fruits each day,choosing whole grains over those that are processed(refined),and limiting consumption of processed and red meats.
(6) Radiations :
Radiation is the most established environmental risk factor for breast cancer.Unnecessary medical X rays chest,and mammograms should always be avoided.Our greatest exposure to radiation is from gamma rays in sunlight hence over exposure to sun and tanning must be restricted.The risk of developing breast cancer from chest radiation is highest if the radiation was given during adolescence when the breasts were still developing.Women who have received high-dose ionizing radiation to the chest (for example,as treatment for other cancers) have a relative risk of breast cancer between 2.1 to 4.0. Radiation after age 40 does not seem to increase breast cancer risk.Nuclear power plants and reactors are other imp. sources of breast carcinogenic radiation.
(7) Hormone Supplements :
Estrogen hormone over exposure naturally (early menarche and late menopause) or artificially in form of menopausal hormone replacement therapy(HRT) put women at increased risk of breast cancer (a relative risk of 1.35 for five or more years of HRT after menopause).Therefore therapy must be at the lowest possible doses for the shortest duration to reach treatment goals.
(8) Drinking Water contaminants :
Some disinfection byproducts of chlorinating water cause breast tumors in rodents as well as humans.Hence over chlorination of water (common practice in Indian community water supply) must be avoided.Water contamination with pesticides and dry cleaning chemicals are also carcinogenic.
(9) Household Chemicals :
Modern household chemicals used in carpeting,furniture,clothing,cookware,cosmetics,lubricants,paints,and adhesives are carcinogenic on their over exposure.In USA PFOA (per fluoro octanoic acid) has been widely detected in blood samples in US,has been found to cause breast cancer in animals.
Solvents used in paint removers, varnishes,wood sealants,fabric cleaners,dry cleaning and septic tank cleaners act as potent carcinogens.
(10) Petrochemical Solvents :
Gasoline,benzene,in fuels are known potent carcinogens.Women working in chemical factories,petrol pumps,,dry cleaning shops,hair dressers,nurses in hospitals and labs,electronic industry workers,have been found to have more cancer breast comparing other women.Benzene has been shown to be a potent breast carcinogen.Benzene exposure mostly originates from air pollution resulting from industrial burning,exhaust and gas fumes,as well as cigarette smoke.Benzene is also found in some nail polishes as well as some nail polish removers.
Drug Pharmaceuticals:
Prolonged use of Reserpine for high BP, Frusemide(Lasix) for kidneys and Anti cancer drugs can sometimes lead to development of breast cancer.
Shampoos,Dyes and Whitening agents :
Dioxane--a contaminant in detergents and shampoos has been proved to cause breast cancer in animals.
(6). Obesity : Gaining weight after menopause can increase a woman's risk A recent study found that putting on 9.9 kg (22 lbs) after menopause increased the risk of developing breast cancer by 18%.
Before menopause your ovaries produce most of your estrogen and fat tissue also produces a small amount of estrogen.After menopause(when ovaries stop making estrogen),most of a woman's estrogen comes from fat tissue.Therefore,having more fat tissue after menopause means more production of estrogen by fat thus raising your blood estrogen levels and so increase in your risk of developing of breast cancer.Also excess fat in your waist area affect risk more than yhe same amount of fat in the hips and thighs.
(7). Lack of physical activity : Evidence is growing that physical activity in form of exercise reduces breast cancer risk.Then how much exercise is needed ?.In one study from Woman's Health Initiative(WHI)...as little as 1.25 to 2.5 hours per week of brisk walking reduced a woman's risk by 18%.Walking 10-15 hours a week reduced the risk a little more.
It is recommended strongly that 45-60 minutes of intentional physical activity 5 or more days a week must be followed to be on safer side.
(8). Night work : Several studies have suggested that women who work at night under artificial lights - for example nurses on night shift-have an increased risk of developing breast cancer--due to change in Melatonin hormone levels(decreased levels in absence of night darkness) which is produced more in darkness by our body.Reduced production of this hormone during night because of artificial light has been shown to predispose to breast cancer in night female-workers.
(9). Pre existent breast disease : Women with denser breast tissue have more glandular tissue and less fatty tissue, and have higher risk of breast cancer.Some non cancerous lesions of breast can later turn into cancer if left untreated.Atypical epithelial or glandular proliferation (hyperplasia) has 2-6 times higher risk of developing cancer breast subsequently.
General Features and Classification :
* Cancer of the breast occurs more often in left breast than the right one. Reason still unknown. In my view it may well be related to most women being right handed and therefore right side breast tissue is constantly on the move and exercised more often because of more use of right pectoralis major muscle in right handed persons. Right breast tissue is hence more oxygenated, more healthier in lifetime and fully developed and stronger than left one ?.
* Each breast is divided into 4 quadrants with the nipple being the central point i.e.above nipple line (horizontally) :upper inner and upper outer quadrants and similarly below nipple line lower inner and lower outer quadrants.Central zone of breast is the zone or area all around the nipple roughly which includes the whole areolar (pink or brown colored round skin area all around nipple) area.
* Upper outer quadrant is the most common area or site of breast from where cancer breast arises in nearly half (50%) of total breast cancers.Therefore, this anatomical area of breast must always be specifically inspected and felt for swellings or any other abnormal change on routine self or clinical examination.
* Central zone of breast is the 2nd most common site of origin of cancer in breast (18-20%)
* Rest 3 quadrants of breast : upper inner (15%), lower outer (11%) and the lower inner is involved in approx. 6% of cases.
* Breast cancer is bilateral (arising in both breasts simultaneously) in 4% of cases or patients.
* 90% 0f breast cancer arise from milk ducts (Duct carcinoma) and only 10% from epithelial or milk producing glandular part (lobule)--(Lobular carcinoma).
Classification :
(1). Duct Cancer (arising from ducts), (2) Lobular Cancer (arising from lobules).
These are further classified as :
(1). In-situ cancer (cancer confined to a duct or a lobule of its origin), (2). Invasive or infiltrating cancer (cancer which has come out of a duct or a lobule and reaching the surroundings).
Duct cancer in-situ : Cancer cells are confined to duct lumen : in one giving an appearance of holes in Swiss-cheese,and in other filling the duct completely.
A=Duct, B=Lobule, C= Dilated duct, D=Nipple, E=Fat, F=Pectoralis muscle, G=Chest wall/Rib cage.
Infiltrating or invasive duct cancer : The cancer cells are seen coming out of the duct of origin and going into surrounding breast tissue.
A,B,C,D, etc are same as above.
Range of ductal cancer.
The above picture shows how duct cancer starts as in-situ cancer (at top) which later on becomes invasive or infiltrating duct cancer (lower picture).
The above picture shows how duct cancer starts as in-situ cancer (at top) which later on becomes invasive or infiltrating duct cancer (lower picture).
Lobular cancer in-situ.
The above picture shows a lobular cancer arising from a lobule and the rounded cancer cells are filling the whole larger round lobule but are still confined within this lobule( i.e. it is lobular cancer in-situ).
(A=Duct, B=Lobule, C= Dilated duct, D=Nipple, E=Fat, F=Pectoralis major muscle, G=Chest wall or rib cage).
Infiltrating /Invasive lobular cancer
The above picture shows the lobular cancer now has come out of its lobule and is infiltrating outside into surrounding tissue ( invasive/infiltrating lobular cancer).
A,B,C,D,E etc. denote as above in previous picture.
There is almost a 100% cure rate for all kinds of in-situ cancers of breast, may it be a ductal or lobular in type.
Tumor/Cancer Heterogeneity :
Every cell of breast cancer originated from the same mother cell.One cell turns into 2 cells, two cells to 4,and so on. By the time a one cm size cancer is detected,the millions of cells that make up the lump have become distant relatives,as different from each other as you may be from your 3rd cousin twice removed.
Such cancer cell diversity represented by the red stars,blue circles and green triangles in the above illustration -is called "tumor heterogeneity". Because what kills one kind of cell might pass over another,hence we need treatments in combination or in sequence,working in different ways,that together may eliminate all of the cancer cells.This is possible now, fortunately, in breast cancer by "molecular targeted therapy".
Breast cancer is the 1st cancer type for which molecular targeted therapy became available,and the success of the approach promises further dramatic advances.
Signs and Symptoms of Breast Cancer :
Breast cancer may or may not cause symptoms. Some women may discover the problem themselves, while others may have the abnormality first detected on a screening exam. Breast pain is not a common symptom of breast cancer. Some of the possible signs and symptoms include:
- Non-painful lumps or masses.
- Lumps or swelling under the arms.
- Nipple skin changes or discharge.
- Changes in the feel, size, or shape of the breast tissue.
(1). A breast lump or mass or thickening that feels different from the surrounding breast tissue.
The above picture shows right breast slightly larger in size than left with a bulge by the lump in the upper-outer quadrant of breast.
* Cancer lumps are usually painless and firm to hard and irregular to feel.
* Cancer lumps are usually not freely mobile and fixed to surroundings.
(2). Bloody discharge from the nipple.
(3). Change in size or shape of breast.
The above picture shows right breast larger in size than left with right nipple at a lower level pointing downwards and a bulge by lump in u-o quadrant.
(4). Retraction or inversion of nipple.
(6). Peeling or flaking 0r thickening of nipple skin.
"Peau d'orange" appearance of breast in all the three pictures above.( Redness or pitting of skin over the breast,like the skin of an orange ( Peau d'orange).
Stages of Breast Cancer :
(Photographs courtesy Mayo Clinic)
Stage of your breast cancer depends upon 3 factors :
(1). Size of your breast lump or tumor (diameter in cms),easy comparison with photograph below :
(2). Local spread of the cancer outside the breast into nearby ipsilateral armpit or axilla and or the collar bone.
(3). Distant spread of the cancer in other parts/areas of the body.
*******************
Stage 0 : All in-situ cancers ( cancers just confined inside to their site of origin i.e. either a duct or a lobule).
Stage I : (1).Tumor or lump up to 2 cms in diameter.
(2).No local spread outside breast to axilla /axillary or clavicular nodes.
(3).No distant spread.
Stage II : (1).Tumor or lump of 2-5 cms size.
(2).No local spread outside breast.
(3).Local spread seen with lump size less than 2 cms.
(3).No distant spread.
Stage III : (1).Tumor or lump of more than 5 cms diameter or size.
(2).Local spread outside breast present into the same side axillary or collar bone lymph nodes.
(3).No distant spread seen.
Stage IV : (1).Tumor or lump of any size.
(2).Local spread outside breast present.
(3).Distant spread to other parts of body always present.
Five year survival rates in Breast Cancer :
Five year survival means the cancer patient lives for a minimum of 5 years with medical treatment after diagnosis of the disease.
(1).Stage 0 ................ 100%
(2).Stage I ................. 100%
(3).Stage II ................. 86%
(4).Stage III ............... 57%
(5).Stage IV ................ 20%
How to diagnose breast cancer ?. / Investigations :
( THREE STEPS TO BREAST HEALTH )
(I). Breast Self Examination (BSE ),
(II). Professional Breast Examination (PBE), and
(III). Mammography plus FNAC.
(I). Breast Self Examination : (most imp)
It is important to know before doing self examination that the two breasts of an individual are never identical,comparing right to left.One is invariably a little larger,slightly different in shape and location on chest wall.The nipples are likewise never identical,but show minor differences in size,location and orientation.
Few women really want to do breast self exam.,and for many the experience is frustrating--you may feel things but do not know what they mean.However,the more you examine your breasts,the more you will learn about them and the easier it will become to point out anything abnormal.
To recognize changes in the way your breasts look like and feel, do a thorough breast self examination at the same time each month.
Examine yourself several days after your periods end when your breasts are least likely to be swollen and tender (mid cycle time is ideal). If you are no longer having periods,choose a day that's easy to remember,such as the 1st or the last day of the month.
Once you know how your breasts feel and look like normally,you can detect even minor changes.
Don't panic if you think you have a lump.Most women have some lumps or lumpy areas in their breasts all the time.In general,only 20- 25% of women who have a suspicious lump biopsied turn out to have breast cancer.
Breasts tend to have different "neighborhoods".The upper and outer area--near your armpit--tends to have the most prominent lumps and bumps.The lower half of your breast can feel normally like a sandy or pebbly beach. The area under the nipple normally can feel like a collection of large grains.Another part may normally feel like a lumpy bowel of oatmeal.
What's important is that you get to know the look and feel of your breasts' various neighborhoods.Does something stand out as different from the rest (like a rock on a sandy beach) ? .Has anything changed ?.
Bring to the attention of your doctor any changes in your breasts that last over a full month's cycle OR seem to get worse or more obvious over time.
It is not unusual for lumps to appear at certain times of the monthly cycle,but then disappear ,as your body changes with the menstrual cycle (if you are still menstruating).Only changes that last beyond one full cycle,or seem to get bigger or more prominent in some way,need your doctor's attention.
Step 1 : Begin by looking at your breasts in the mirror with your shoulders straight and your arms on your sides and then arms on your hips(pressing hands on your hips).Look for :
** Breasts that are their usual size,shape and color.
** Breasts that are evenly shaped without visible distortion or swelling.
2. A nipple that has changed position or become inverted (pushed inwards instead of sticking out).
3. Redness,soreness,rash or swelling anywhere on your breast including nipples
Step 2 and 3 : Raise your arms up above your head,clasp your hands behind your neck and look for or check for the same changes again.
While you are at the mirror, gently squeeze each nipple between your thumb and forefinger to check for any nipple discharge which could be a milky or yellow fluid or a bloody discharge.(kindly note that a drop or two of clear or whitish fluid is normal).
Step 4. : Lie down and place a pillow under the shoulder of the breast you're examining.Keep the arm on that side raised as shown in figure.
Mentally divide the breast area into strips or circles.The area should include your collar bone above to your bra line below and your breast bone or your cleavage in the center to your underarm /armpit on sides.
Feel your breast by using your right hand to feel for your left breast, and left hand to feel the right breast.Feel with the sensitive pads of your three middle fingers held flat.
Use a firm,smooth touch keeping the fingers flat and together with small circular or rotational movements to cover each area of strip or circle.Go over each area three times using varying degrees of pressure as shown.
Use light pressure to feel for changes below the skin and deeper pressure to feel for changes in the breast tissue.
Step 5 : Finally feel your breasts while you are standing or sitting.Many women find that the easiest way to feel their breasts is when their skin is wet and slippery,so they like to do and can do this step in the shower (Hands glide easily over wet,soapy skin).Cover your entire breast with same hand movements as in step 4.
(II). Professional Breast Examination :
Contact tour doctor immediately if you note any abnormal change in your breasts.
In addition, professional exams.are recommended at least 1-3 years for women between the ages of 20 and 40, and annually thereafter.Ask your doctor or nurse any questions you may have about breast health or self-exams.techniques.
Professional Investigations :
(1). Thorough local examination of breast by the doctor,
(2). FNAC (Fine Needle Aspiration Cytology),
(3). Needle or Trucut Biopsy, if FNAC is inconclusive.
(4). Open Surgical Biopsy or Lumpectomy (rarely needed when both FNAC and Needle biopsies are inconclusive).
(5) Mammography,
(6) X-Rays,CT scans etc.to scan the whole body once diagnosis of cancer is established.
(III). Mammography :
Mammography is a safe,low dose x-ray technique that creates images of the inside of the breast.Mammography can detect lumps before they can be felt,so it is an imp. screening procedure.Have a screening mammogram by age 40.From age 40 to 49,have one every 1-2 years,then annually from age 50 on wards.
Biggest misconception about mammography is that it picks up every breast cancer.In fact,mammogram misses at least 10% of breast cancers. So if you feel a lump that doesn't show up on mammogram,bring it to your doctor's attention and get it evaluated.
Treatment of Breast Cancer
Treatment and outcome of breast cancer depends upon the stage of the disease at the time of diagnosis.Stage-0 (in situ cancer) is 100% curable,whereas stage -I disease is also nearly completely cured with modern day advance therapies.
Treatment of breast cancer is multifaceted comprised of a combination of :
(1). Surgery (Mastectomy--Removal of Breast).
(2). Chemotherapy.
(3). Radiotherapy.
Modified Radical Mastectomy (most common surgery).
The areas/breast tissue shaded pink in above picture is surgically excised along with B and C groups of axillary lymph nodes.
A - Pink highlighted area--tissue removed.,
B - Armpit lymph nodes-Level I.,
C - Armpit lymph nodes-Level II.,
D - Armpit lymph nodes-Level III.
In recent years there has been an explosion of life saving treatment advances against breast cancer, bringing new hope and excitement. Instead of one or two options as used to be earlier, today there is an overwhelming menu of treatment choices that fight the complex mixture of cells in an individual cancer.
Molecular targeted chemotherapy has further revolutionized the treatment outcome of breast cancer these days. Breast cancer is the first cancer type for which molecular targeted therapy has been used and the outcomes are wonderful even in stage II and III cases